- Product
-
Solution
-
By Industry
Cybersecurity solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
-
- Resources
-
Books
Our ultimate guides and playbooks
Solution Briefs
Overview of PureDome’s functionality
-
Quizzes
Assess your cybersecurity readiness
Case Studies
PureDome customer success stories
Newsletter
Subscribe to the PureDome newsletter
-
- About Us
- Partner
- Pricing
- Download
Ultimate Guide to Remote Workers Security 2024
-
Aiman Ikram
-
25 Apr 2024
- 3 min read


Remote work has become the new norm, but with convenience comes security risks. This guide provides essential strategies to protect your remote workforce in 2024.
What is Remote Work Security?
Approximately 22 million employed adults aged 18 and above in the United States engage in full-time remote work and this raises concerns regarding remote work security. Remote work security is all about keeping your work and data safe while working from anywhere. It involves protecting sensitive information from cyber threats like hacking, phishing, and malware attacks.

This means setting up secure connections, using strong passwords, and being cautious about what you share online. It's also about staying updated on the latest security practices and being vigilant against potential risks.
Traditional remote work security focused on VPNs and network perimeters. Now, with a hybrid workforce, advanced cybersecurity practices are essential. Here are the three main pillars of remote and hybrid work security:
- Secure access to SaaS apps for both work and personal use in remote environments
- Defense against threats from general web access, like personal email or cloud storage
- Application management of corporate software across on-premise and cloud platforms using zero trust network access (ZTNA)
Remote Work Cybersecurity Key Insights
- iPhone users (17%) face a higher risk of hacking compared to Android users (12%) among remote workers.
- Co-working spaces (18%) are identified as the top vulnerable spots for data theft.
- 21% of remote workers who operate from foreign countries experienced theft of work-related information.
- Cyberattacks on remote workers lead to costs exceeding $10,000 for almost 25% of companies.
What are the Key Cyber Security Risks of Working Remotely?
Here are the top 5 cybersecurity risks of working remotely:
- Phishing Attacks: Hackers often use phishing emails or messages to trick remote workers into revealing sensitive information like login credentials or financial data.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks in cafes, airports, or hotels can be easily compromised, exposing remote workers to potential data breaches or unauthorized access.
- Malware and Ransomware: Without the protection of corporate firewalls and antivirus software, remote devices are more vulnerable to malware and ransomware attacks, which can result in data loss or financial extortion.
- Endpoint Security: Remote devices like laptops or smartphones may lack adequate security measures, making them easy targets for cyberattacks that exploit vulnerabilities in operating systems or applications.
- Data Leakage: Remote work increases the risk of unintentional data leakage through insecure file sharing, unauthorized access to cloud storage, or improper handling of sensitive information. This leads to compliance violations or reputational damage for organizations.
How to Maintain Security When Employees Work Remotely?
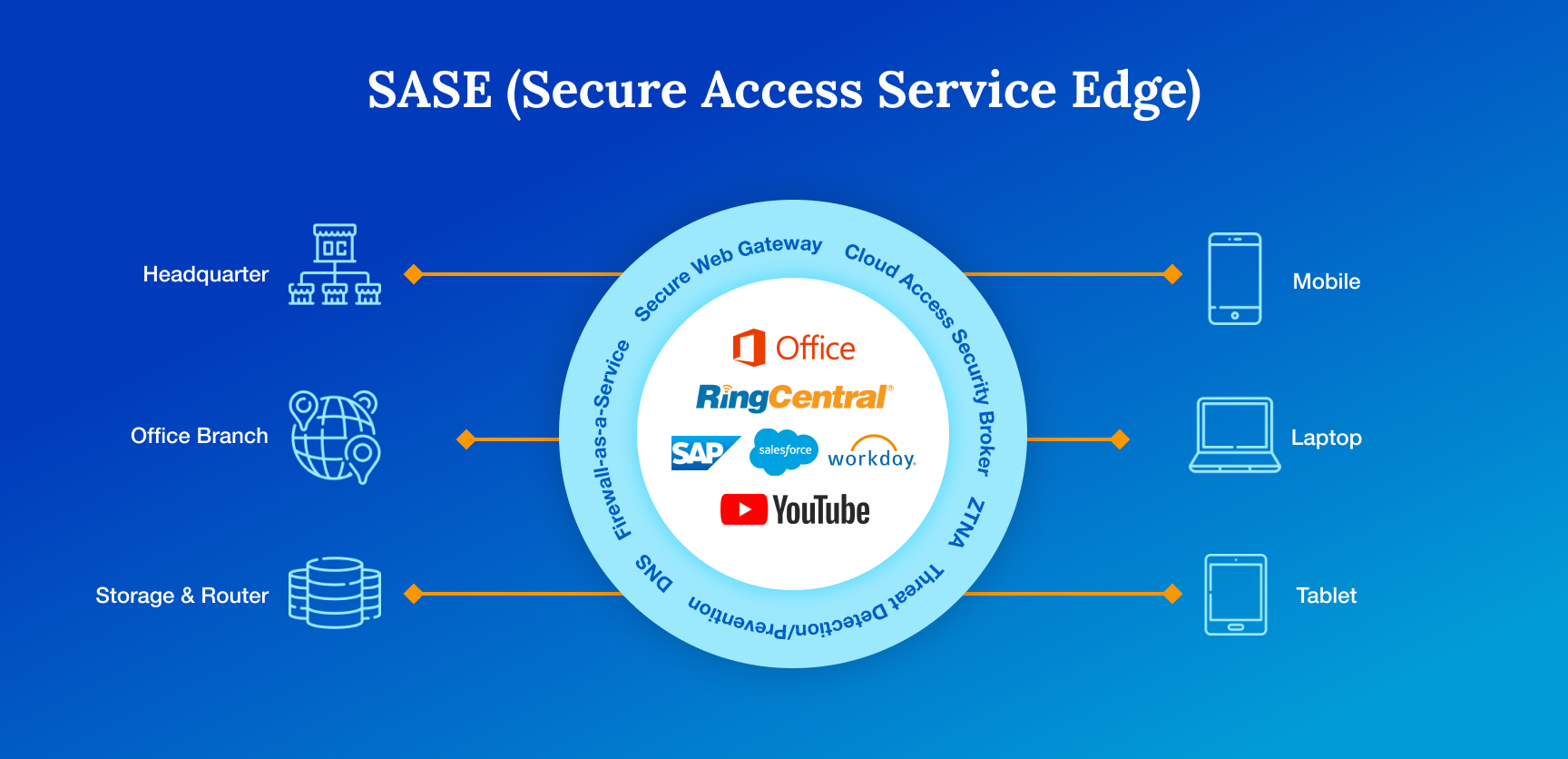
-
Implement Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Utilize ZTNA principles to verify every user and device trying to access company resources, regardless of their location, ensuring secure connections and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Provide Secure Remote Access: Equip employees with secure remote access tools like virtual private networks (VPNs) or secure access service edge (SASE) solutions to encrypt data transmitted over public networks and protect against interception.
-
Enforce Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords, requiring additional verification steps like biometrics or one-time codes to ensure only authorized users gain access.
-
Regularly Update Software and Devices: Maintain regular updates for software, operating systems, and devices to patch known vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats, reducing the risk of exploitation by cyber attackers.
-
Educate Employees on Security Best Practices: Provide ongoing training and awareness programs to educate employees about cybersecurity risks, phishing scams, and safe remote work practices, empowering them to identify and avoid potential threats.
-
Monitor and Audit Remote Access: Implement monitoring and auditing tools to track remote access activities, detect suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts, and respond promptly to security incidents to mitigate potential damage.
Emerging Trends in Remote Work Security
Secure Collaboration Tools: Use encrypted communication and file-sharing platforms to ensure that all remote work interactions are protected.
Cloud Security Solutions: Implement advanced cloud security measures to protect data stored and accessed in cloud environments.
Employee Security Training: Regularly train employees on the latest security best practices and how to recognize potential threats, such as phishing attacks.
Practical Tips for Remote Workers
Secure Your Home Network: Use strong passwords and encryption for your Wi-Fi.
Recognize Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of suspicious emails and messages, and don't click on unknown links.
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system and applications to protect against vulnerabilities.
Use a VPN: Connect to a Virtual Private Network to encrypt your internet connection.
Lock Your Devices: Always lock your computer and other devices when not in use to prevent unauthorized access.
Why Does Your Organisation Need a Remote Security Policy?
In 2024, having a remote security policy is crucial to protect your organization's data and defend against cyber threats. It establishes clear guidelines for secure remote work, ensuring everyone understands how to work safely from any location. Without this policy, your organization is at a higher risk of data breaches and other security issues.
Implementing robust security measures is essential to safeguard your valuable information. Adopt these recommended practices now to enhance your security posture and protect your organization from potential threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can PureDome help protect remote workers from cybersecurity threats?
PureDome offers advanced threat detection and protection services, monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities and providing real-time alerts to mitigate potential security breaches. This keeps remote workers safe from cyber threats.
What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and how does it enhance remote security?
ZTNA verifies every user and device attempting to access company resources, regardless of their location, ensuring secure connections and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
What are the best practices for securing personal devices used for remote work?
Best practices include using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, keeping software and devices updated, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks, and using a ZTNA solution for secure connections when accessing company resources remotely.