
It's astonishing how much the medical industry has changed in the last few decades. Clinics and medical facilities have transformed operations from having entirely paper-based processes in the 70s to adopting interconnected, high-tech systems today. The growth of telehealth services, including innovations like virtual medical assistants, is also crucial to this transformation.
Telehealth leverages technology for remote medical services, presenting benefits and challenges, with privacy risks being a primary concern. As data flows become increasingly globalized, a strong understanding of global privacy laws is imperative. To address this, establishing strong privacy measures is crucial for fostering trust and securing patient data in healthcare, including information handled by virtual assistants.
As Millwood stated, “For telehealth to succeed, privacy and security risks must be identified and addressed.”
How Major Privacy Laws Address Health Data?
The healthcare industry is experiencing a substantial surge in data accumulation from various regions worldwide. According to most local and global data privacy regulations, a significant portion of the data related to an individual's health is categorized as personal or sensitive information.
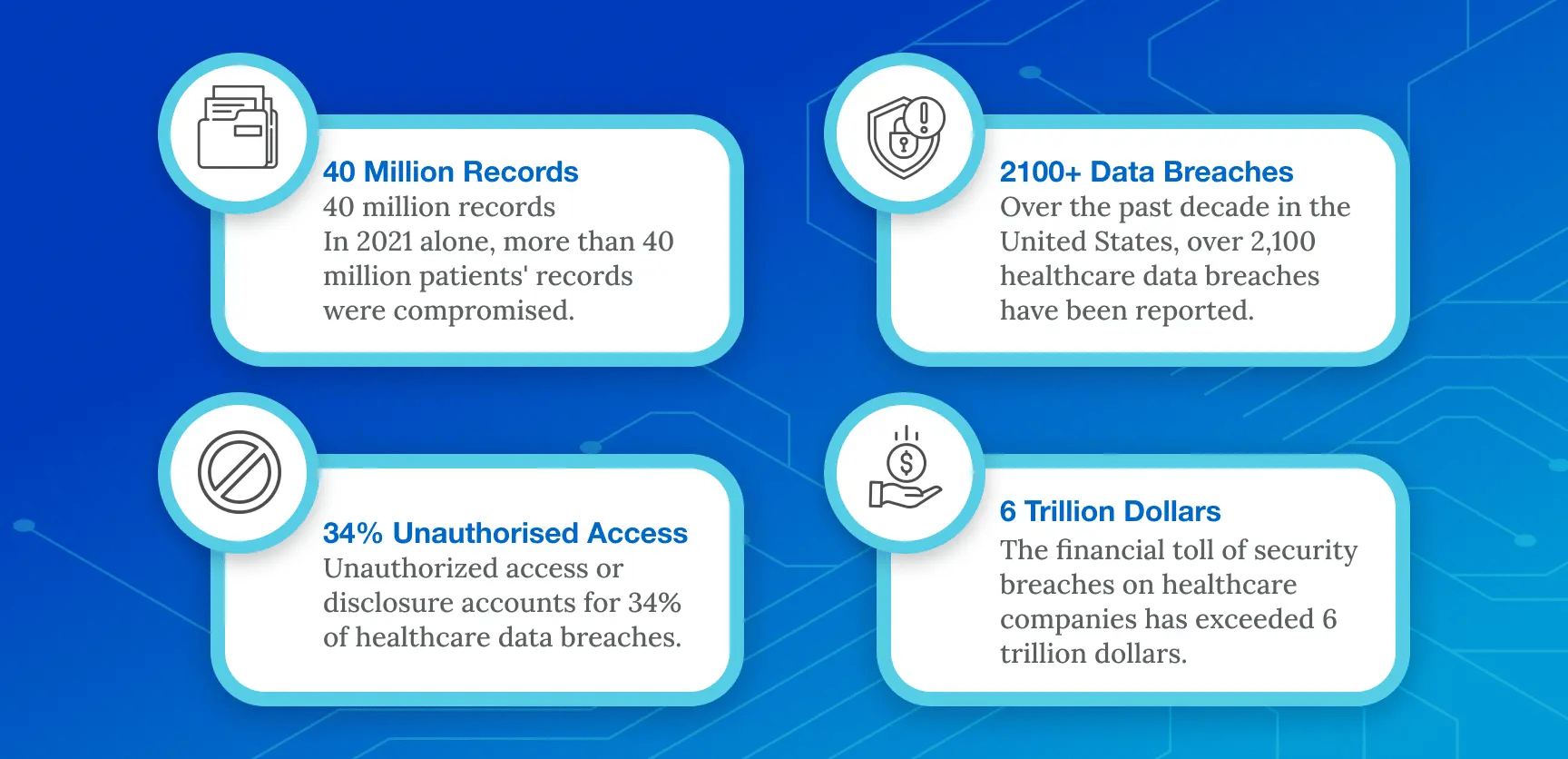
With the escalation of cybersecurity attacks and incidents of data breaches, the healthcare sector is notably one of the industries facing severe consequences.
How can VMAs Meet Healthcare Data Compliance Requirements?
In the healthcare industry, you rely on gathering, using, and managing patient data, especially as a significant part of it is transitioning to digital formats, making it susceptible to cyber threats. Your increasing dependence on Virtual Medical Assistants (VMAs) to streamline daily operations highlights your crucial need to establish secure protocols, particularly when digitally transmitting this data across networks.
The anticipated growth of virtual assistance in healthcare at a CAGR of 15.6% from 2022 to 2031 means a continuous increase in your patient data transfer and online hosting. While this trend isn't alarming, it underscores the importance of ensuring your VMAs comply with healthcare security regulations to safeguard patient data confidentiality and integrity.
Let's explore how you can ensure VMAs comply with international data privacy regulations.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
In the United States, health data protection is primarily governed by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). HIPAA sets standards to protect sensitive patient information, requiring organizations handling protected health information (PHI) to implement and adhere to essential physical, network, and procedural security measures.
The primary objective of the HIPAA Privacy Rule is to shield individuals' health information while permitting the necessary flow of data to ensure and enhance high-quality healthcare. It also aims to safeguard public health and well-being. Entities covered by HIPAA, including providers, health plans, and clearinghouses, along with their business associates like VMA agencies, are obligated to adhere to the HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules.
Here's how virtual medical assistants can ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations:
| HIPAA Rules | What steps can VMAs take to ensure compliance? |
|---|---|
| Privacy Rule | Restrict access to patient information solely to authorized healthcare professionals. Implement secure authentication methods and ensure that virtual assistants adhere to strict guidelines for handling and transmitting sensitive health data. |
| Security Rule | Ensure secure and encrypted channels are used to transmit electronic PHI (ePHI). Implement robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against unauthorized access, and regularly update and back up systems to prevent data breaches. |
| Breach Notification Rule | Establish a clear and efficient protocol for identifying and responding to potential breaches in virtual assistant systems. This includes notifying affected individuals and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) within the required timeframe. |
| Enforcement Rule | Conduct routine assessments to identify and address compliance issues specific to virtual assistants. Provide comprehensive training for staff overseeing virtual healthcare assistants and establish a systematic internal HIPAA compliance audit process. |
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) governs safeguarding health data in Europe. This EU law on privacy and data protection applies to all member states, regulating the handling of personal data and its transfer beyond the EU and EEA regions. Healthcare data compliance with the GDPR is mandatory for healthcare providers and telemedicine platforms operating within the EU. For virtual healthcare assistants and AI-powered platforms specializing in healthcare services within the EU, compliance with GDPR is critical.
Here's how virtual medical assistants can ensure adherence to key GDPR principles:
| GDPR Principle | What steps can VMAs take to ensure compliance? |
|---|---|
| Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency | Clearly communicate to users how their data will be utilized and obtain explicit consent before initiating any data collection. |
| Purpose limitation | Collect only the necessary data for the provision of healthcare services and refrain from using acquired data for purposes unrelated to healthcare. |
| Data minimization | Limit data collection to what is strictly essential for delivering healthcare assistance, avoiding unnecessary gathering of information. |
| Accuracy | Regularly update and verify user data to maintain its precision. Implement systems for correcting inaccuracies and outdated information. |
| Storage limitation | Retain user data only for the duration necessary for providing healthcare assistance. Enforce a data retention policy and routinely purge unnecessary data. |
| Integrity and confidentiality (security) | Utilize secure and encrypted channels for transmitting user data. Implement robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and potential breaches of data security. |
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
In Canada, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) governs private sector entities engaged in collecting, using, or disclosing personal information for commercial purposes. This includes physicians operating in private practices who receive direct payment from patients or reimbursement from provincial health plans or employment insurance plans.
PIPEDA extends beyond medical data to encompass various personal information such as age, name, ID numbers, income level, ethnicity, credit records, loan records, and social status.
For virtual medical assistants operating within Canada, it is essential to comply with PIPEDA. Here's how these virtual assistants can ensure adherence to key PIPEDA principles:
| PIPEDA Principle | What steps can VMAs take to ensure compliance? |
|---|---|
| Accountability | Designate a data protection officer or a similar role overseeing compliance with PIPEDA principles. |
| Identifying Purposes | Communicate to patients the reasons for collecting their data, preferably before or at the time of data collection. |
| Consent | Obtain explicit consent from patients before collecting their data, ensuring they fully understand how their data will be used. |
| Limiting Collection | Collect only the data necessary for providing healthcare assistance, avoiding the acquisition of extraneous information. |
| Limiting Use, Disclosure, and Retention | Use patient data for the purposes stated during data collection. Do not disclose or use data for other purposes without patient consent or legal requirements. Retain data only for the necessary duration. |
| Accuracy | Regularly update and verify patient data to maintain its accuracy. Implement systems to rectify inaccuracies and manage outdated information. |
| Safeguards | Employ secure and encrypted channels for data transmission and storage. Implement robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and potential data breaches. |
Australia - Privacy Act 1988
The Privacy Act 1988 serves as the principal legislation for privacy protection in Australia. Encompassing thirteen Australian Privacy Principles (APPs), the Privacy Act applies to certain private sector entities and most Australian and Norfolk Island Government agencies. The Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC) conducts oversight and enforcement of compliance with the Privacy Act.
virtual medical assistants and telemedicine platforms operating in Australia are required to comply with the Privacy Act. Here's how they can align with the key Australian Privacy Principles:
| Australian Privacy Principle (APP) | What steps can VMAs take to ensure compliance? |
|---|---|
| APP 1: Open and Transparent Management | Maintain a transparent and easily accessible privacy policy outlining the handling of patient data. |
| APP 2: Anonymity and Pseudonymity | Provide patients with the option to remain anonymous or use a pseudonym whenever possible. |
| APP 3: Collection of Solicited Personal Information | Collect patient data exclusively for the explicit purpose of providing healthcare services and ensure lawful collection methods. |
| APP 4: Dealing with Unsolicited Personal Information | If unsolicited personal information is received, assess its lawfulness. If not lawful, either destroy it or ensure it is de-identified. |
| APP 5: Notification of the Collection of Personal Information | Inform patients at the time of collection about the information being collected, the reasons for collection, and how it will be used. |
| APP 6: Use or Disclosure of Personal Information | Use personal data solely for the purpose for which it was collected unless the patient provides consent for another purpose. |
| APP 11: Security of Personal Information | Implement robust security measures to safeguard patient data against unauthorized access, modification, loss, and disclosure. |
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The central privacy legislation in California is the CCPA, which was enacted on January 1, 2020. The CCPA provides extensive safeguards for consumer data, making it one of the most comprehensive privacy laws in the United States. It applies to any for-profit business in California that gathers consumers' personal data and meets specific criteria related to annual gross revenues, the volume of personal data processed, or the percentage of annual revenue generated from the sale of consumers' personal data.
virtual medical assistants and telemedicine platforms operating within California must ensure compliance with the CCPA. Here are measures these entities can adopt:
| CCPA Right | What steps can VMAs take to ensure compliance? |
|---|---|
| Right to Know | Maintain transparency by informing patients about collected data, its source, purpose, disclosure or sale, and recipients. |
| Right to Delete | Implement systems allowing patients to request the deletion of their personal data. Fulfill requests promptly unless legal reasons mandate retention. |
| Right to Opt-Out | If, by exception, personal data is sold to third parties (unlikely in healthcare due to regulations), provide patients with a clear method to opt out. |
| Right to Non-Discrimination | Ensure patients are not subject to discrimination when exercising CCPA rights. This includes not denying services, applying different pricing, or providing varying service levels based on a patient's decision to exercise their rights. |
| Right to Access | Establish a mechanism for patients to request and receive information about the categories and specific pieces of their personal information collected in the past 12 months. |
Wrapping Up
In the transformative landscape of healthcare driven by telemedicine and technology, virtual medical assistants (VMAs) play a crucial role as part of the medical team, sharing responsibilities equivalent to the onsite employees. To consistently meet regulatory standards, you must ensure that VMAs seamlessly incorporate global regulatory compliance into their daily operations. This proactive approach ensures that they remain compliant, regardless of their customers' locations, thereby upholding the highest standards of healthcare worldwide.